画像をダウンロード r rna types 230315-What are rrna
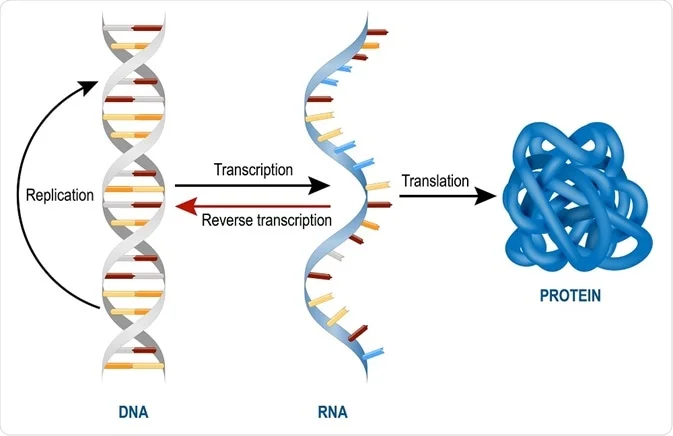
An RNAbased vaccine therefore acts as a code to instruct the body to make many copies of the virus protein—and the resulting antibodies—itself, resulting in an immune response Unlike more traditional vaccines, RNAbased vaccines are also beneficial in that they eliminate the need to work with the actual virusDNA is only two types intra nuclear and extra nuclear Three different types of RNA mRNA, tRNA and rRNA 15 Its quantity is fixed for cell The quantity of RNA of a cell is variable 16 It is long lived Some RNAs are very short lived while others have somewhat longer life 17If DNA is a protein "blueprint," then think of the RNA as the "architect" that reads the blueprint and carries out the building of the protein There are different types of RNA that have different functions in the cell These are the most common types of RNA that have an important role in the functioning of a cell and protein synthesis

Alyvea Com Transcription And Translation Biology Lessons Biology Classroom
What are rrna
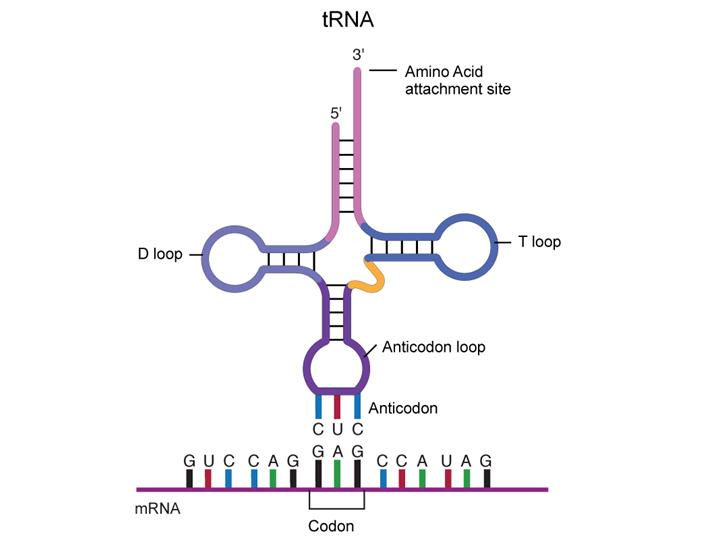
What are rrna-Transfer RNA is the third main type of RNA and one of the smallest, usually only 70–90 nucleotides long It carries the correct amino acid to the site of protein synthesis in the ribosome It is the base pairing between the tRNA and mRNA that allows for the correct amino acid to be inserted in the polypeptide chain being synthesized (Figure 4)RRNA – The ribosomal RNA or the rRNA produces ribosomes with the ribosomal


Rna Structure Function Synthesis Types And Interference Earth S Lab
Genetic rearrangements were also observed in other types of RNA viruses, including influenza virus, a minusstrand RNA virus, in retroviruses, and in doublestranded Φ6 bacteriophage The following genomes of plant RNA viruses reveal RNA rearrangements alfalfa mosaic virus (AlMV), beet necrotic yellow vein virus (BNYVV), bromoviruses (seeTransfer RNA is the third main type of RNA and one of the smallest, usually only 70–90 nucleotides long It carries the correct amino acid to the site of protein synthesis in the ribosome It is the base pairing between the tRNA and mRNA that allows for the correct amino acid to be inserted in the polypeptide chain being synthesized (Figure 4)There are currently two primary types of COVID19 tests being used to test patients for COVID19 molecular tests (also known as nucleic acid, RNA or PCR tests) and rapid antigen tests
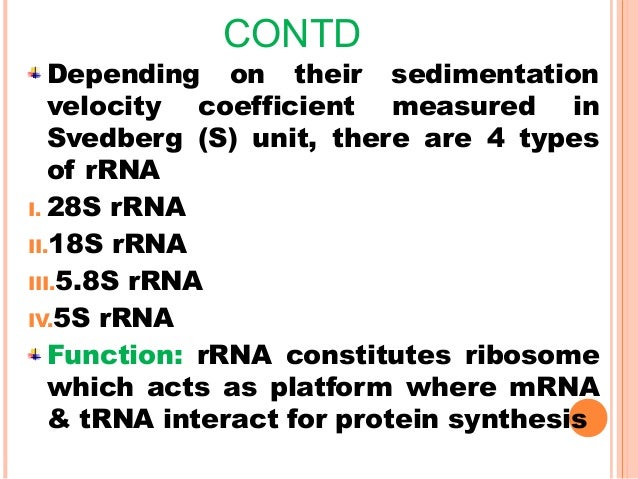
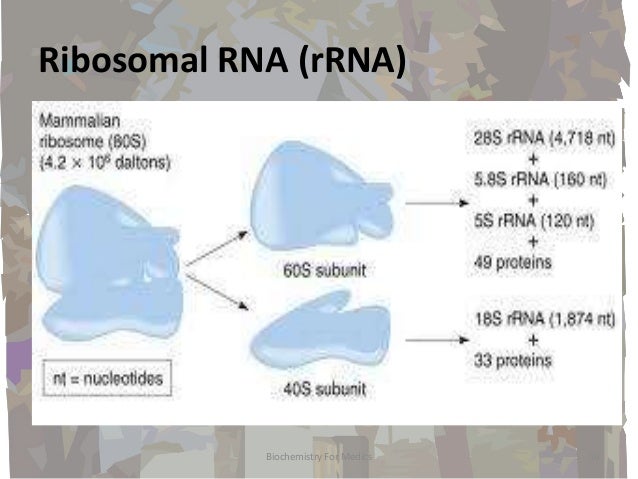
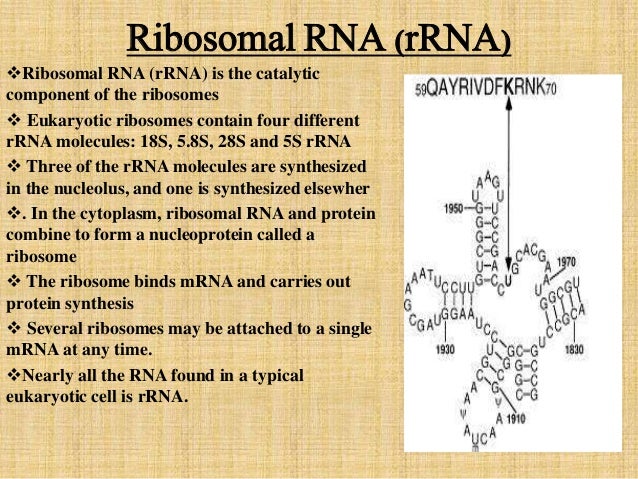
Types of Ribosomal RNA Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic ribosomes are made of a larger and smaller subunit and these two units come together during mRNA translation The smaller subunit in prokaryotes is made of an RNA molecule about 1500 nucleotides in length with a Svedberg coefficient of 16STypes of RNA In both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, there are three main types of RNA – messenger RNA (mRNA), ribosomal RNA (rRNA), and transfer RNA (tRNA) These 3 types of RNA are discussed belowAn RNAbased vaccine therefore acts as a code to instruct the body to make many copies of the virus protein—and the resulting antibodies—itself, resulting in an immune response Unlike more traditional vaccines, RNAbased vaccines are also beneficial in that they eliminate the need to work with the actual virus
Types of RNA 3 Replication Structure of Ribose Nucleic Acids It is also a polynucleotide but the pentose ribose has a free hydroxyl group in position 2′ It is a long chain polynucleotide which exist in a regular conformation like a doublechain DNA although some viruses eg, reoviruses and wound tumour virus) have double stranded RNAThe exact manufacturing and delivery process of RNA vaccines can vary depending on the type Types of RNA vaccine Nonreplicating mRNA The simplest type of RNA vaccine, an mRNA strand is packaged and delivered to the body, where it is taken up by the body's cells to make the antigenThere are currently two primary types of COVID19 tests being used to test patients for COVID19 molecular tests (also known as nucleic acid, RNA or PCR tests) and rapid antigen tests


Different Types Of Rna Amp Translation


Rna Structure Functions And Types Of Rna
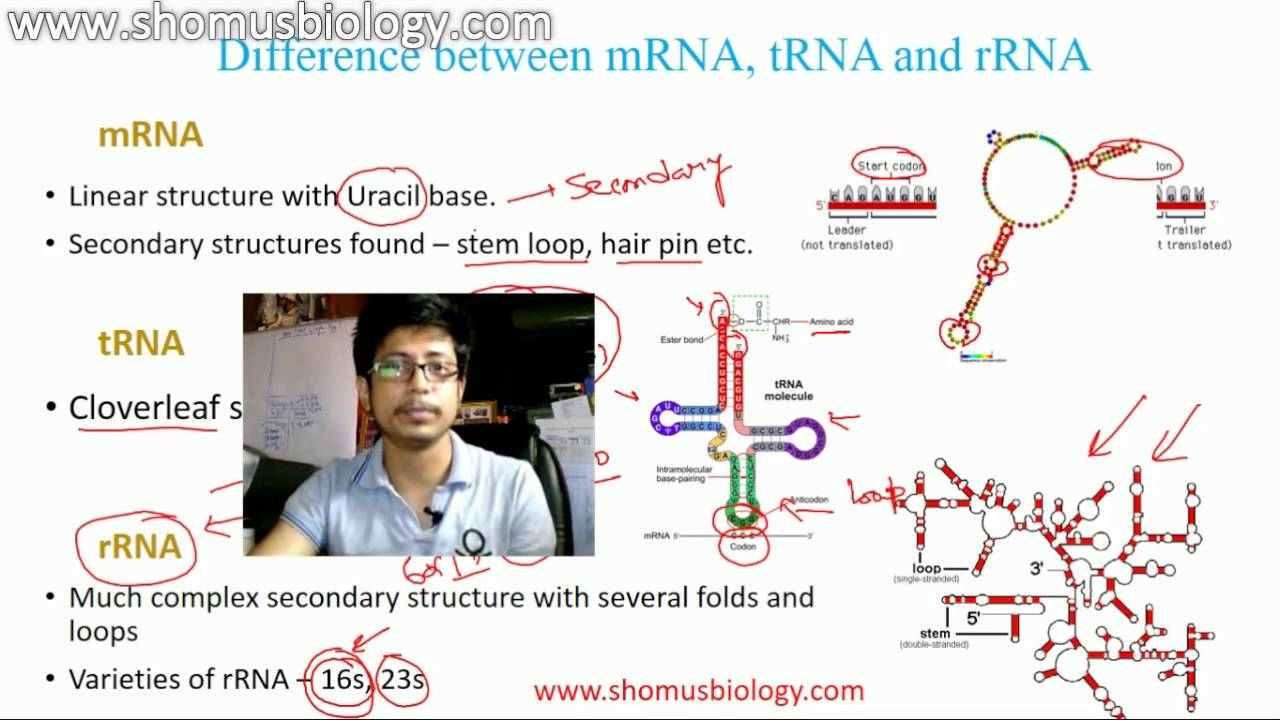
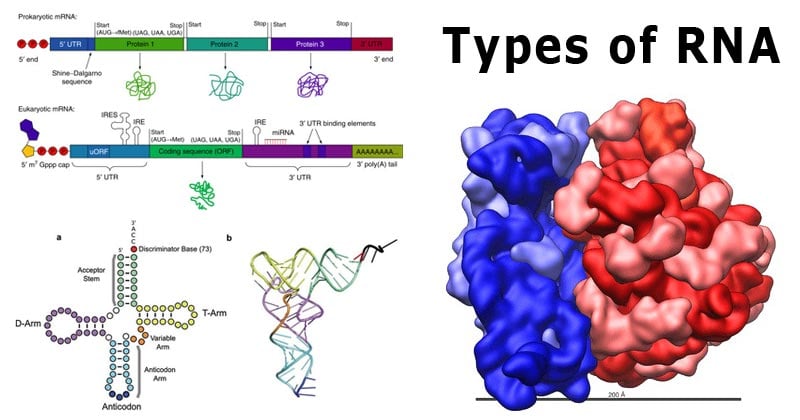
There are three types of RNA found in the cell and they are Messenger RNA (mRNA) Transfer RNA (tRNA) Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) 1 Messenger RNA (mRNA) Only a few percent of total cellular RNA is mRNA (only about 5%) It is a linear, singlestranded molecule with 5' and 3' endsAfter the RNA folds into its tertiary structure, it is Lshaped, with the acceptor stem and Tarm forming an extended helix and the anticodon loop and Darm similarly making another extended helix These two helices align perpendicularly to each other in a way that brings the Darm and Tarm into close proximity while the anticodon loop and theOne of the most recent has about 34 RNA and DNA vaccines on the list But so far none have been approved for use in humans Compared to conventional vaccines There are many different types of



Dna Transcription And Translation Review There Are 3 Types Of Rna Messenger Rna Mrna Ribosomal Rna Rrna Transfer Rna Trna Ppt Download


Rna Properties Structure Types And Functions Molecular Biology Microbe Notes
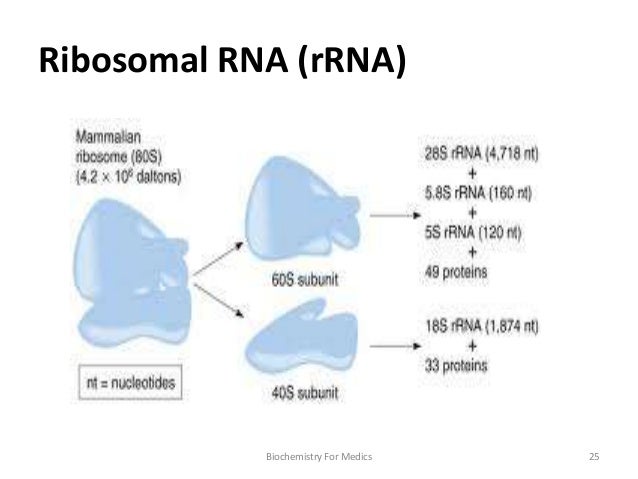
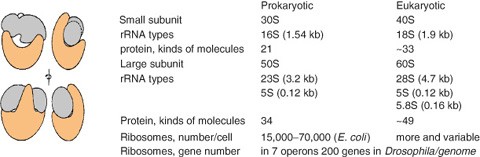
Bacteria have 3 rRNAs The small subunit contains 16S rRNA ~1500 nt, and the large subunit contains 5S (1 nts) and 23S (2900 nts) the "S" denotes a sedimentation coefficient these names were applied in the 1960s, long before any sequencing wAn RNAbased vaccine therefore acts as a code to instruct the body to make many copies of the virus protein—and the resulting antibodies—itself, resulting in an immune response Unlike more traditional vaccines, RNAbased vaccines are also beneficial in that they eliminate the need to work with the actual virusRibosomal RNA multiple families 5S rRNA 5S ribosomal RNA RF 58S rRNA 58S ribosomal


Q Tbn And9gcsn Ckqhmhinuuf1a0exe3h3nhgtktdn9tcgrzbmvn 1npnaj J Usqp Cau


Fact Sheet Dna Rna Protein Microbenet The Microbiology Of The Built Environment Network
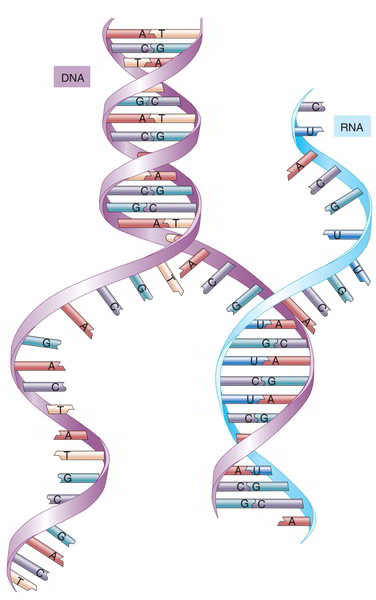
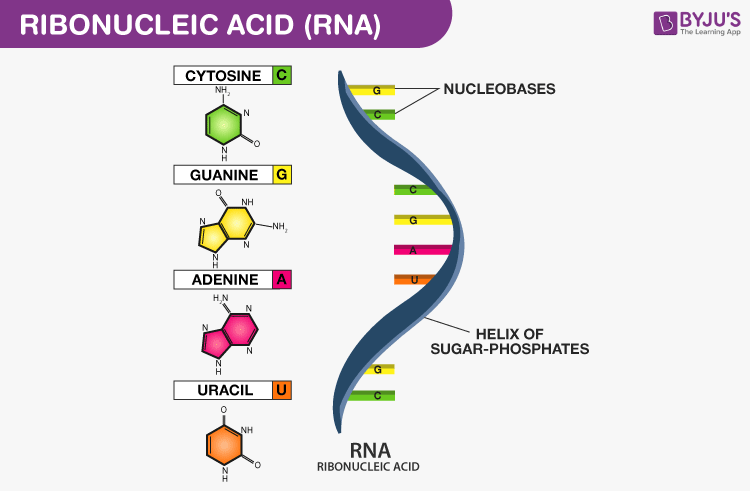
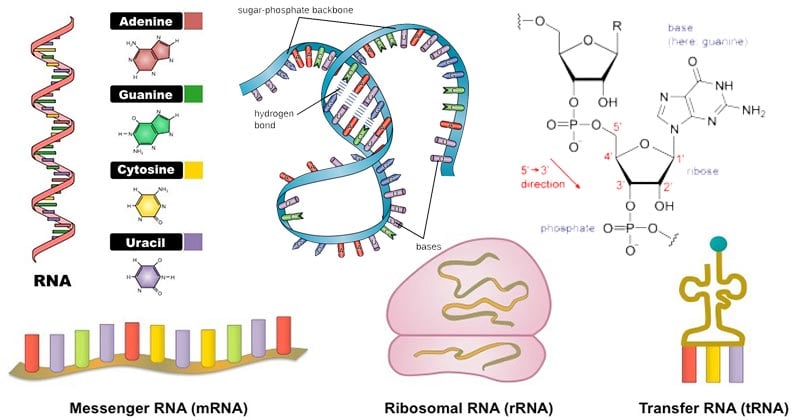
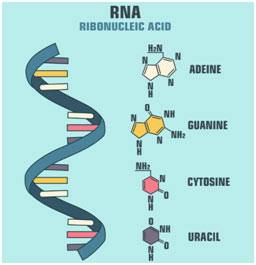
RNA is an acronym for ribonucleic acid, a nucleic acidMany different kinds are now known RNA is physically different from DNA DNA contains two intercoiled strands, but RNA only contains one single strandRNA also contains different bases from DNA These bases are the following (A) Adenine (G) Guanine (C) Cytosine (U) Uracil Adenine forms bonds with uracil, and guanine forms bonds withRNA is an acronym for ribonucleic acid, a nucleic acidMany different kinds are now known RNA is physically different from DNA DNA contains two intercoiled strands, but RNA only contains one single strandRNA also contains different bases from DNA These bases are the following (A) Adenine (G) Guanine (C) Cytosine (U) Uracil Adenine forms bonds with uracil, and guanine forms bonds withThis type of RNA is found in some viruses When these viruses infect eukaryotic cells, the dsRNA can interfere with normal RNA function and stimulate an interferon response Circular singlestrand RNA (circRNA) has been found in both animals and plants At present, the function of this type of RNA is unknown


What Is The Mechanism Of Synthesis Of Trna And Rrna Quora
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-185759552-51db7df6ee41476780f3f768b9793781.jpg)


What Is The Most Abundant Form Of Rna
The main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic RNA polymerase is that prokaryotes have a single type of RNA polymerase, whereas eukaryotes have three main types of RNA polymerases Furthermore, prokaryotic RNA polymerase contains five subunits while in eukaryotes, RNA polymerase I transcribes rRNA genes, RNA polymerase II transcribes mRNA genes, and RNA polymerase III transcribes smallRibosomal RNA (rRNA), molecule in cells that forms part of the proteinsynthesizing organelle known as a ribosome and that is exported to the cytoplasm to help translate the information in messenger RNA (mRNA) into protein The three major types of RNA that occur in cells are rRNA, mRNA, and transfer RNA (tRNA)Numerous key discoveries in biology have emerged from studies of RNA (ribonucleic acid), including seminal work in the fields of biochemistry, genetics, microbiology, molecular biology, molecular evolution and structural biologyAs of 10, 30 scientists have been awarded Nobel Prizes for experimental work that includes studies of RNA Specific discoveries of high biological significance are



Figure 2 From Expression Of Distinct Maternal And Somatic 5 8s 18s And 28s Rrna Types During Zebrafish Development Semantic Scholar



Rrna High Res Stock Images Shutterstock
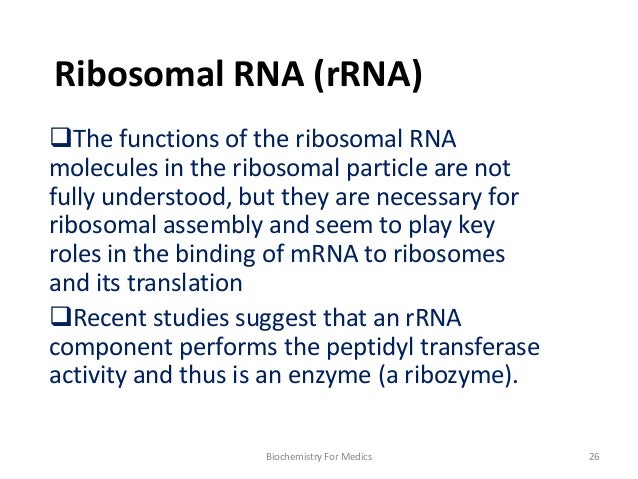
Ribosomal RNA Definition Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is the RNA component of ribosomes, the molecular machines that catalyze protein synthesisRibosomal RNA constitute over sixty percent of the ribosome by weight and are crucial for all its functions – from binding to mRNA and recruiting tRNA to catalyzing the formation of a peptide bond between two amino acidsTypes of RNA and their roles The type of RNA dictates the function that this molecule will have within the cell Aside from the coding region of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules that will beAn RNA vaccine or mRNA (messenger RNA) vaccine is a type of vaccine that uses a copy of a natural chemical called messenger RNA (mRNA) to produce an immune response The vaccine transfects molecules of synthetic RNA into immunity cellsOnce inside the immune cells, the vaccine's RNA functions as mRNA, causing the cells to build the foreign protein that would normally be produced by a pathogen



Rna Structure Function Synthesis Types And Interference Earth S Lab


Rna Structures Types And Functions
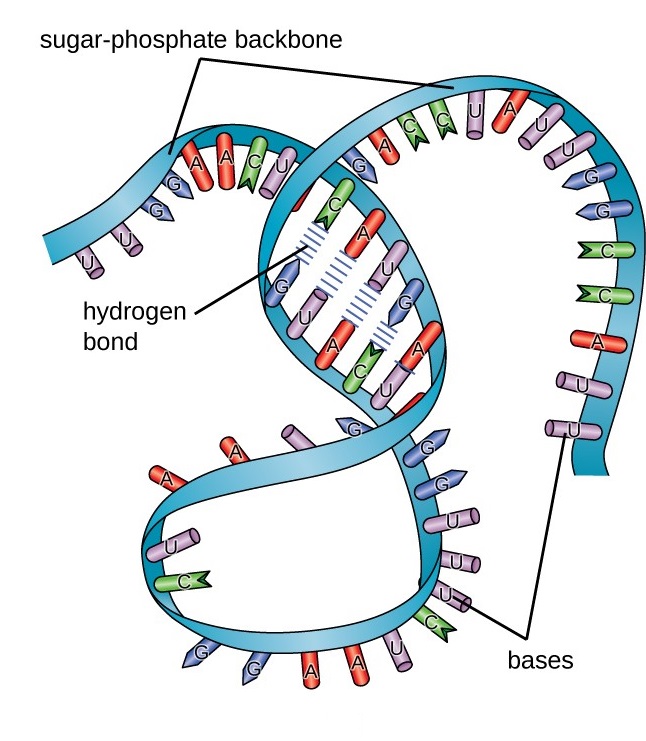
Types of RNA Structure of RNA The primary structure of RNA is the same as that of DNA It is also a polynucleotide chain with 5′3′ sugar phosphate links But the sugar is ribose and generally it exists as a singlestranded molecule For that reason, it does not have the onetoone ratio between the complementary basesRNA A polymer of ribonucleotides, is a single stranded structure There are three major types of RNA m RNA,t RNA and r RNA Besides that there are small nuclear,micro RNAs, small interfering and heterogeneous RNAs Each of them has a specific structure and performs a specific functionTransfer RNA (tRNA), small molecule in cells that carries amino acids to organelles called ribosomes, where they are linked into proteins In addition to tRNA there are two other major types of RNA messenger RNA (mRNA) and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) By 1960 the involvement of tRNAs in the assembly of



A Beginners Guide To Working With Rna Part 1 Background Edinburgh Crf Genetics Core



06 Picture Of 3 Types Of Rna Biology Notebook
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of noncoding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from ribosomal DNA (rDNA) and then bound to ribosomal proteins to form small and large ribosome subunits rRNA is the physical and mechanical factor of the ribosomeIf DNA is a protein "blueprint," then think of the RNA as the "architect" that reads the blueprint and carries out the building of the protein There are different types of RNA that have different functions in the cell These are the most common types of RNA that have an important role in the functioning of a cell and protein synthesis1 DNA/RNAbased DNA and RNA vaccines use fragments of genetic material made in the lab These fragments code for a part of the virus (such as its spike protein)After the vaccine is injected


Fact Sheet Rrna In Evolutionary Studies And Environmental Sampling Microbenet The Microbiology Of The Built Environment Network



Ribosomal Rna Wikipedia
Types of RNA Structure of RNA The primary structure of RNA is the same as that of DNA It is also a polynucleotide chain with 5′3′ sugar phosphate links But the sugar is ribose and generally it exists as a singlestranded molecule For that reason, it does not have the onetoone ratio between the complementary basesRNA virus A virus in which the genetic material is RNA The RNA may be either double or singlestranded There are 6 classes of viruses The DNA viruses constitute classes I and II The RNA viruses make up the remaining classes Class III viruses have a doublestranded RNA genomeThe following are the types of RNA wherein each type is encoded by its own type of gene tRNA– The transfer RNA or the tRNA carries amino acids to ribosomes while translation;


Fact Sheet Rrna In Evolutionary Studies And Environmental Sampling Microbenet The Microbiology Of The Built Environment Network



Structure And Function Of Rna Microbiology
Messenger RNAs, also known as mRNA, are one of the types of RNA that are found in the cell This particular one, like most RNAs, are made in the nucleus and then exported to the cytoplasm where the translation machinery, the machinery that actually makes proteins, binds to these mRNA molecules and reads the code on the mRNA to make a specific proteinA second type of RNA helps form the structure of a ribosome This type of RNA is called ribosomal RNA, or rRNA Remember that DNA and RNA differ slightly at the nucleotide level Therefore, theIf DNA is a protein "blueprint," then think of the RNA as the "architect" that reads the blueprint and carries out the building of the protein There are different types of RNA that have different functions in the cell These are the most common types of RNA that have an important role in the functioning of a cell and protein synthesis



Different Types Of Rrna Repeat Unit In Microsporidia And In Download Scientific Diagram


Central Dogma Of Biology Course Hero
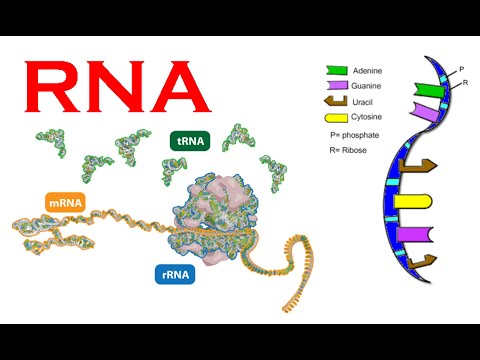
There are three types of RNA found in the cell and they are Messenger RNA (mRNA) Transfer RNA (tRNA) Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) 1 Messenger RNA (mRNA) Only a few percent of total cellular RNA is mRNA (only about 5%) It is a linear, singlestranded molecule with 5' and 3' endsMost heterogeneous of the 3 types of RNA in terms of both base sequence and size It carries the genetic code copied from the DNA during transcription in the form of triplets of nucleotides called codons As part of posttranscriptional processing in eukaryotes, the 5' end of mRNA is capped with a guanosine triphosphate nucleotide, whichTypes of RNA Structure of RNA The primary structure of RNA is the same as that of DNA It is also a polynucleotide chain with 5′3′ sugar phosphate links But the sugar is ribose and generally it exists as a singlestranded molecule For that reason, it does not have the onetoone ratio between the complementary bases



Rna Structure Types And Functions



Hwrk 3 Quesitons Flashcards Quizlet
The types of RNA are 1 Transfer RNA (tRNA) 2 Messenger RNA (mRNA) and 3RNA polymerase III is a type of eukaryotic RNA polymerase enzyme that is responsible for the transcription of ribosomal 5S rRNA, tRNA and other small RNAs This is the enzyme that catalyzes the transcription of all housekeeping genes that are required in all cell types and in most environmental conditionsRNA Polymerase Definition A RNA polymerase (RNAP), or ribonucleic acid polymerase, is a multi subunit enzyme that catalyzes the process of transcription where an RNA polymer is synthesized from a DNA template The sequence of the RNA polymer is complementary to that of the template DNA and is synthesized in a 5'→ 3′ orientation


Biol60 Gene Expression Transcription



Types Of Rna Bioninja
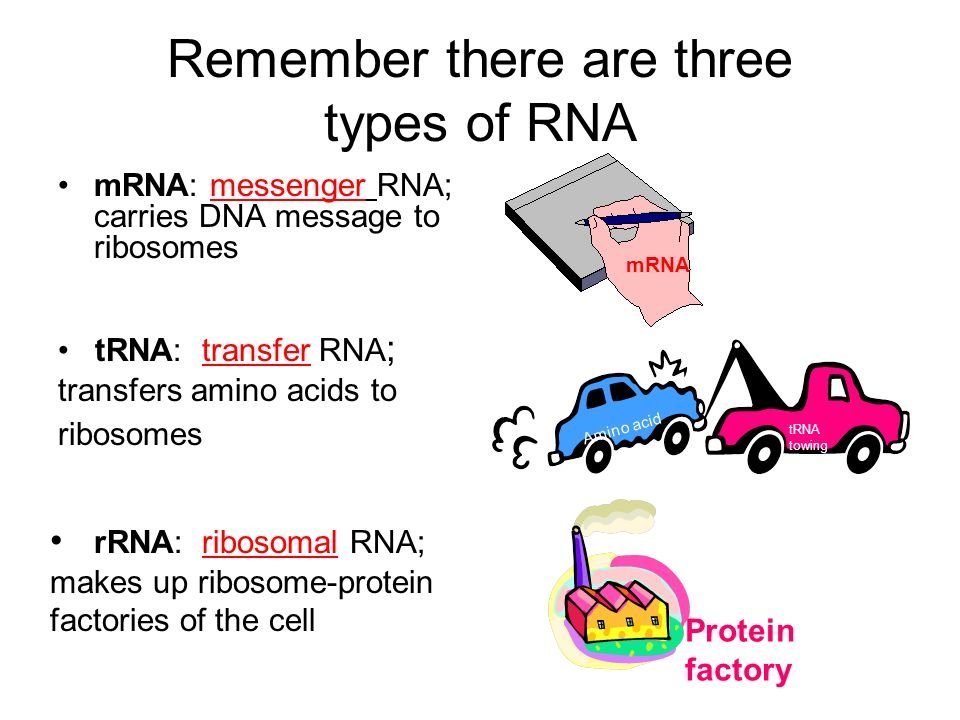
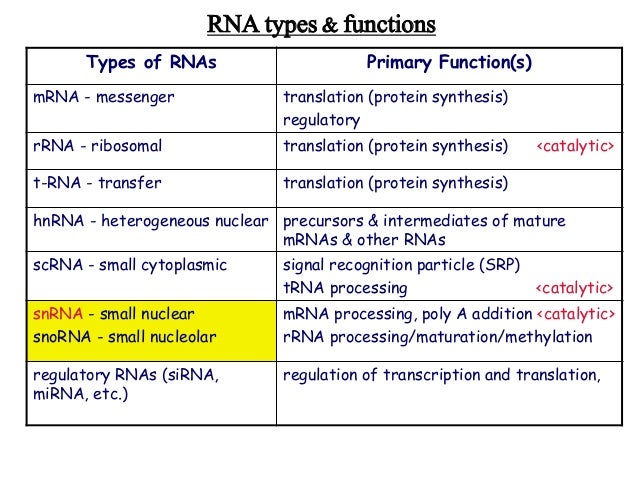
RNA A polymer of ribonucleotides, is a single stranded structure There are three major types of RNA m RNA,t RNA and r RNA Besides that there are small nuclear,micro RNAs, small interfering and heterogeneous RNAs Each of them has a specific structure and performs a specific functionMRNA – The messenger RNA or the mRNA encodes amino acid sequences of a polypeptide;The 3 Types of RNA and Their Functions They are messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA, and transfer RNA


Difference Between Rna And Mrna Definition Types Function Differences



Ribosomal Rna Definition Function Britannica
The main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic RNA polymerase is that prokaryotes have a single type of RNA polymerase, whereas eukaryotes have three main types of RNA polymerases Furthermore, prokaryotic RNA polymerase contains five subunits while in eukaryotes, RNA polymerase I transcribes rRNA genes, RNA polymerase II transcribes mRNA genes, and RNA polymerase III transcribes smallThere are three types of RNA, each with a unique function mRNA is used to produce proteins from genes rRNA, along with protein, forms the ribosome, which translates mRNA tRNA is the link between the two other types of RNA


Rna Structure Types And Functions


Difference Between Mrna Trna And Rrna Definition Features Function Similarities And Differences



Ribosomal Rna Wikipedia


Mrna Trna And Rrna Youtube



Ribosomal Rna Rrna Definition Function Biology Dictionary


Solved A The Major Forms Of Rna Are Mrna Rrna And Trna Chegg Com



Compare The Three Types Of Rna Note Significant Similarities And Differences Use The Table Below To Brainly Com



Biology Exams 4 U 11 Different Types Of Rna In A Cell



Differences Between Rna And Dna Types Of Rna Mrna Trna Rrna Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Which Type Of Rna Is The Most Important Of All Quora



Rna And Transcription



Sections 3 4 Structure Of Rna Made Of Nuleotides Three Differences Between Dna Rna Sugar Dna Deoxyribose Sugar Rna Ribose Sugar Rna Is Single Stranded Ppt Download



Rrna Sequence Function Synthesis Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Types Of Rna Ribonucleic Acid Simplified Biology


Rna Types Biochemistry Medbullets Step 1


The Principal Kinds Of Rna And Their Structures



Ribosomal Rna Wikipedia


Types Of Rna Mrna Rrna And Trna


What Are The Differences Between Mrna Trna And Rrna Quora


Rna Structure Types Mrna Trna Rrna And Functions



Alyvea Com Transcription And Translation Biology Lessons Biology Classroom



Types Of Noncoding Rnas Ncrnas Noncoding Rnas Are Classified Into Download Scientific Diagram


Rna Properties Structure Types And Functions Molecular Biology Microbe Notes



Ribosomal Rna Definition Function Britannica


8



Rna Types Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation
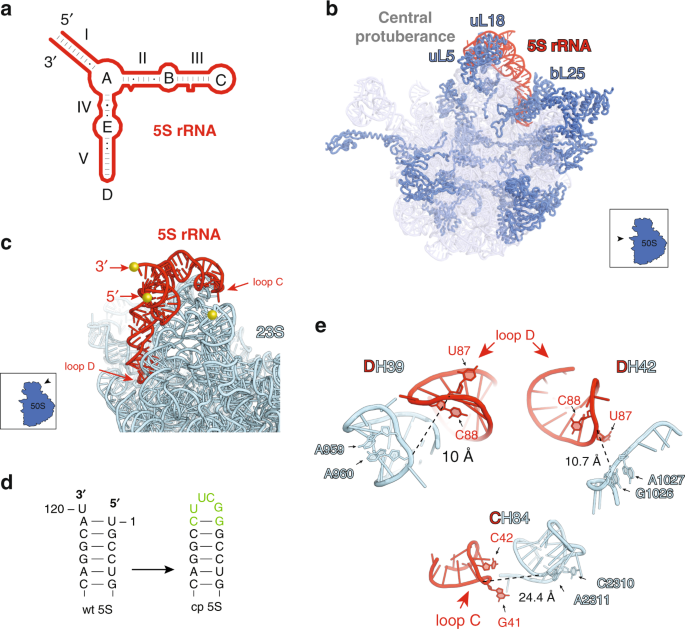


Ribosome Engineering Reveals The Importance Of 5s Rrna Autonomy For Ribosome Assembly Nature Communications


Plos One Modified Rna Seq Method For Microbial Community And Diversity Analysis Using Rrna In Different Types Of Environmental Samples



5s Rrna Variant Types And Their Expression In Zebrafish A Download Scientific Diagram


Rna Definition Types Structure And Functions Biology Educare


Frontiers Non Coding Rna What Is Functional And What Is Junk Genetics



Ribosomal Rna An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



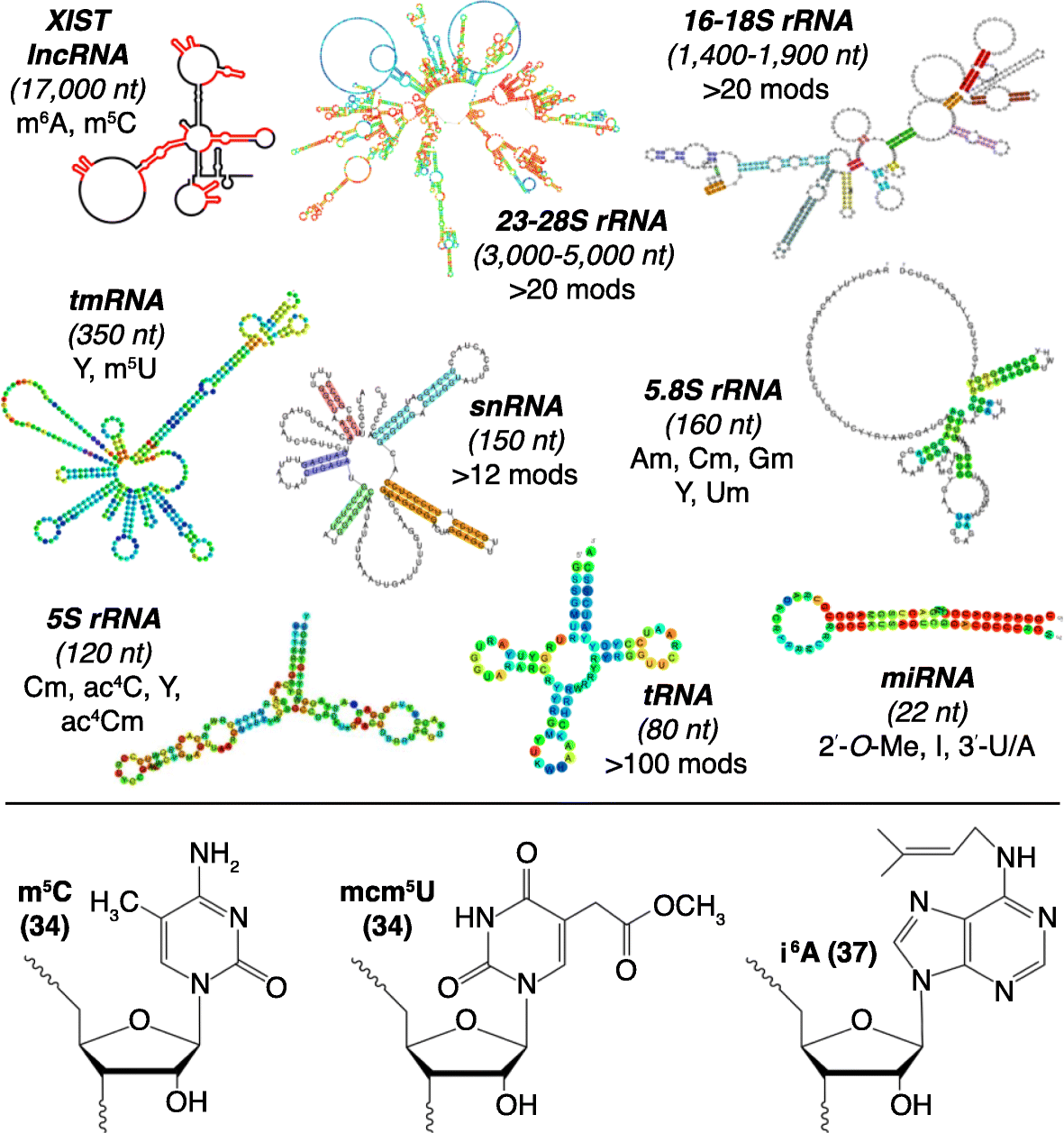
Landscape Of Trna Rrna And Mrna Modifications Associated With Rna Download Scientific Diagram


C0nc0rdance There Aren T Three Types Of Rna Types Of Rna That Exist Mrna Trna Rrna Microrna Rnai Pre Mrna Asrna Shrna Mrprna Tasirna Lncrna Tsrna Tmrna Srp Rna Snrna Grna Snorna Dsrna


Compbio Rna Folding
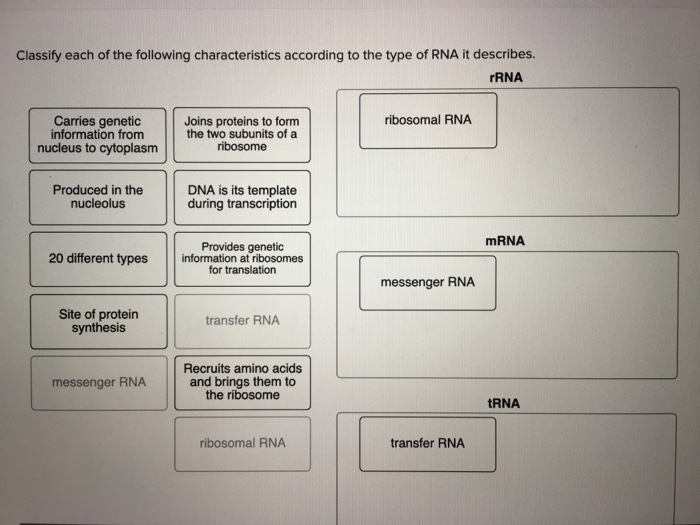


Solved Classify Each Of The Following Characteristics Acc Chegg Com


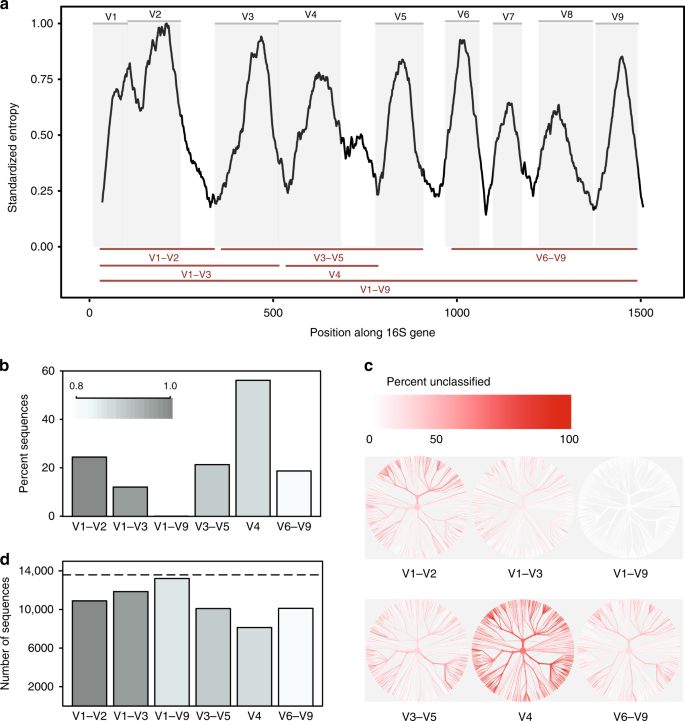
16s Rrna And 16s Rrna Gene Ezbiocloud Help Center


What Is The Mechanism Of Synthesis Of Trna And Rrna Quora


14 2 Overview Of Transcription Biology Libretexts


3



Rna Definition Structure Types Functions Britannica



Ribosomal Rna An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Structure Function And Types Of Rna Mrna Trna Rrnalncrna Mirna Si Medical Laboratory Technician General Biology Medical Questions


Structure Types And Function Of Rna
/RNA-58de78835f9b58468365a9fa.jpg)


The 3 Types Of Rna And Their Functions
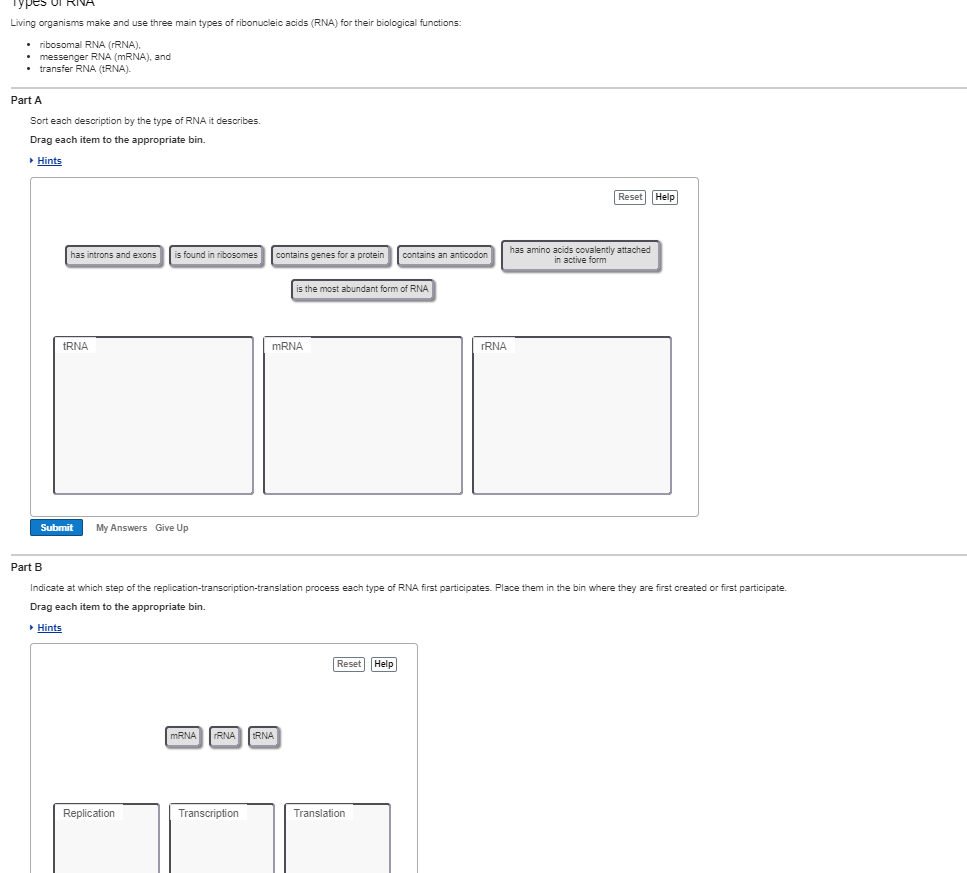


Solved Living Organisms Make And Use Three Main Types Of Chegg Com


5 5 Rna Human Biology



Ribosomal Rna Wikipedia


Ribonucleic Acid



Hwrk 3 Quesitons Flashcards Quizlet
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/150955162-56a2b3ea3df78cf77278f383.jpg)


4 Types Of Rna The Architect Of Proteins



Ribosomal Rna Definition Function Britannica


5s Ribosomal Rna Wikipedia


Rna Structure Types And Functions


Difference Between Mrna Trna And Rrna Knowswhy Com


Q Tbn And9gcsnnf X7mag0luevkk4gakv Vo3vq G2ayf N2li1iynvfv Cgw Usqp Cau


Lifestyle Modifications Coordinating The Trna Epitranscriptome With Codon Bias To Adapt Translation During Stress Responses Genome Biology Full Text


7 Types Of Rna With Structure And Functions Microbe Notes


Evaluation Of 16s Rrna Gene Sequencing For Species And Strain Level Microbiome Analysis Nature Communications



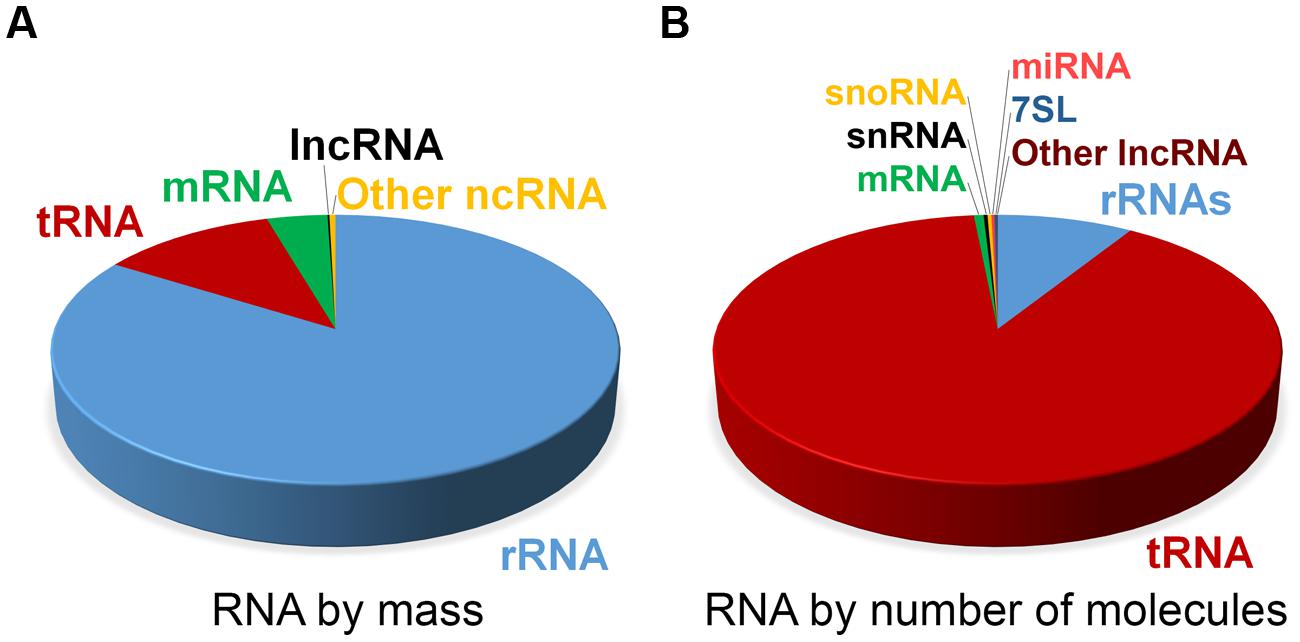
Types And Size Distribution Of Human Rna The Different Types Of Human Download Scientific Diagram


Rna Structure And Function



Solved Match The Following Statements With The Three Majo Chegg Com



Ribosomal Rna An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


Ribosomes Springerlink


7 Types Of Rna With Structure And Functions Microbe Notes


Types Of Rna Mrna Rrna And Trna



Rna For The Mcat Everything You Need To Know Shemmassian Academic Consulting


Ldi Rna Binding Proteins


Rna Structure And Synthesis And Types Youtube



Mrna Trna And Rrna Function Types Of Rna Youtube



10 3 2 Three Types Of Rna Youtube



5 Types Of Rna Mrna Trna Rrna Hnrna And Snrna Youtube



Differences Between Rna And Dna Types Of Rna Mrna Trna Rrna Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
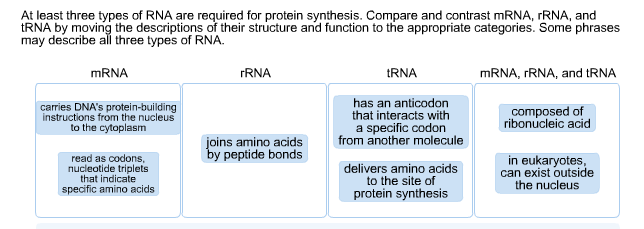


Solved At Least Three Types Of Rna Are Required For Prote Chegg Com



All About Ribosome Youtube
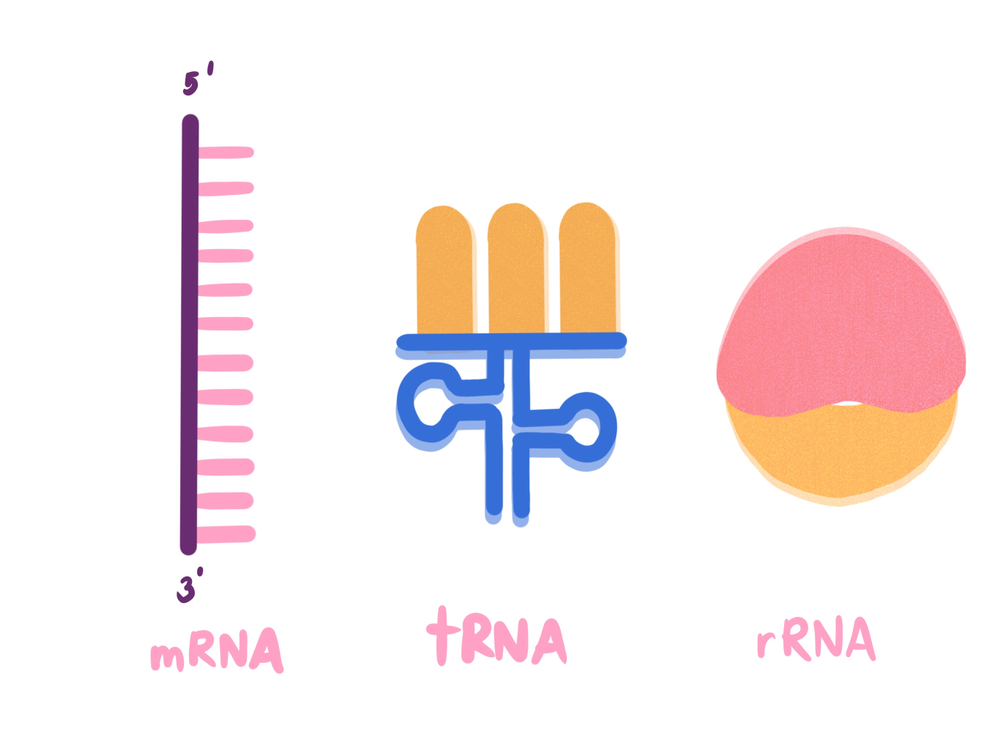


What Is Rna What Does Rna Do



Rna Ck 12 Foundation


コメント
コメントを投稿